HTML
Chapter 5.Images
Adding Images
To add an image into the page you need to use an < img> element. This is an empty element (which means there i no closing tag). It must carry the following two attributes:
src This tells the browser where it can find the image file. This will usually be a relative URL pointing to an image on your own site.
alt This provides a text description of the image which describes the image if you cannot see it.
title You can also use the title attribute with the < img> element to provide additional information about the image. Most browsers will display the content of this attribute in a tootip when the user hovers over the image.
JPEG vs PNG vs GIF — which image format to use and when?
Use JPEG format for all images that contain a natural scene or photograph where variation in colour and intensity is smooth. Use PNG format for any image that needs transparency or for images with text & objects with sharp contrast edges like logos. Use GIF format for images that contain animations.
JPEG is a lossy compression specification that takes advantage of human perception. It can achieve compression ratios of 1:10 without any perceivable difference in quality. Beyond this, the compression artefacts become more prominent. Because JPEG compression works by averaging out colours of nearby pixels (read Discrete Cosine Transform), JPEG images are best suited for photographs and paintings of natural scenes where the variations in colour and intensity are smooth.
PNG is a lossless image format using DEFLATE compression. No data is lost during compression and no compression artefacts are introduced in the image. For this reason, a PNG image would retain higher quality than an image than JPEG and would look a lot sharper, it would also occupy more space on the disk.
GIF is also a lossless image format that uses LZW compression algorithm. It was favoured over PNG for simple graphics in websites in its early days because the support of PNG was still growing.
Transparency In a simple form, transparency indicates something that is completely invisible. Logos and icons often need to be placed on backgrounds with variable colours. Hence it is desirable, that the background of these logos and icons is made transparent so that a single image can be used over multiple background variations.
JPEG images don’t support transparency and are hence not usable for such cases.
PNG images support transparency in two ways — inserting an alpha channel that allows partial transparency or by declaring a single colour as transparent index transparency.
GIF images support transparency by declaring a single colour in the colour palette as transparent index transparency.
IMAGES Summary:
- The < img> element is used to add images to a web page.
- You must always specify a src attribute to indicate the source of an image and an alt attribute to describe the content of an image.
- You should save images at the size you will be using them on the web page and in the appropriate format.
- Photographs are best saved as JPEGs; illustrations or logos that use flat colors are better saved as GIFs.
Chapter 11.Color
Understanding Color
Every color on a computer screen is created by mixing amounts of red, green, and blue. To find the color you want, you can use a color picker.
Color picking tools are available in image editing programs like Photoshop and GIMP. You can see the RGB values specified next to the radio buttons that say R, G, B. The hex value is provided next to the pound or hash #symbol. There is also a good color picking tool at: colorschemedesigner.com
RGB Values Values for red, green, and blue are expressed as numbers between 0 and 255.
Hex Codes Hex values represent values for red, green, and blue in hexadecimal code.
Color Names Colors are represented by predefined names. However, they are very limited in number.
Hue Hue is near to the colloquial idea of color. Technically speaking however, a color can also have saturation and brightness as well as hue.
Saturation Saturation refers to the amount of gray in a color. At maximum saturation, there would be no gray in the color. At minimum saturation, the color would be mostly gray.
Brightness Brightness (or “value”) refers to how much black is in a color. At maximum brightness, there would be no black in the color. At minimum brightness, the color would be very dark.
COLOR Summary:
- Color not only brings your site to life, but also helps convey the mood and evokes reactions.
- There are three ways to specify colors in CSS: RGB values, hex codes, and color names.
- Color pickers can help you find the color you want.
- It is important to ensure that there is enough contrast between any text and the background color (otherwise people will not be able to read your content).
- CSS3 has introduced an extra value for RGB colors to indicate opacity. It is known as RGBA.
- CSS3 also allows you to specify colors as HSL values, with an optional opacity value. It is known as HSLA.
Chapter 12.Text
Typeface Terminology
Serif Serif fonts have extra details on the ends of the main strokes ofthe letters. These details are known as serifs.
Sans-Serif Sans-serif fonts have straight ends to letters, and therefore have a much cleaner design.
Monospace Every letter in a monospace (or fixed-width) font is the same width. (Non-monospace fonts have different widths.)
Weight
- Light
- Medium
- Bold
- Black
The font weight not only adds emphasis but can also affect the amount of white space and contrast on a page.
Style
- Normal
- Italic
- Oblique
Italic fonts have a cursive aspect to some of the lettering. Oblique font styles take the normal style and put it on an angle.
Stretch
- Condensed
- Regular
- Extended
In condensed (or narrow) versions of the font, letters are thinner and closer together. In expanded versions they are thicker and further apart.
Choosing a Typeface for your Website
Serif Serif fonts have extra details on the end of the main strokes of the letters.
Examples: Georgia Times Times New Roman
Sans-Serif Sans-serif fonts have straight ends to letters and therefore have a much cleaner design. Examples: Arial Verdana Helvetica
Monospace Every letter in a monospace typeface is the same width. (Non-monospace fonts have different widths.) Examples: Courier Courier New
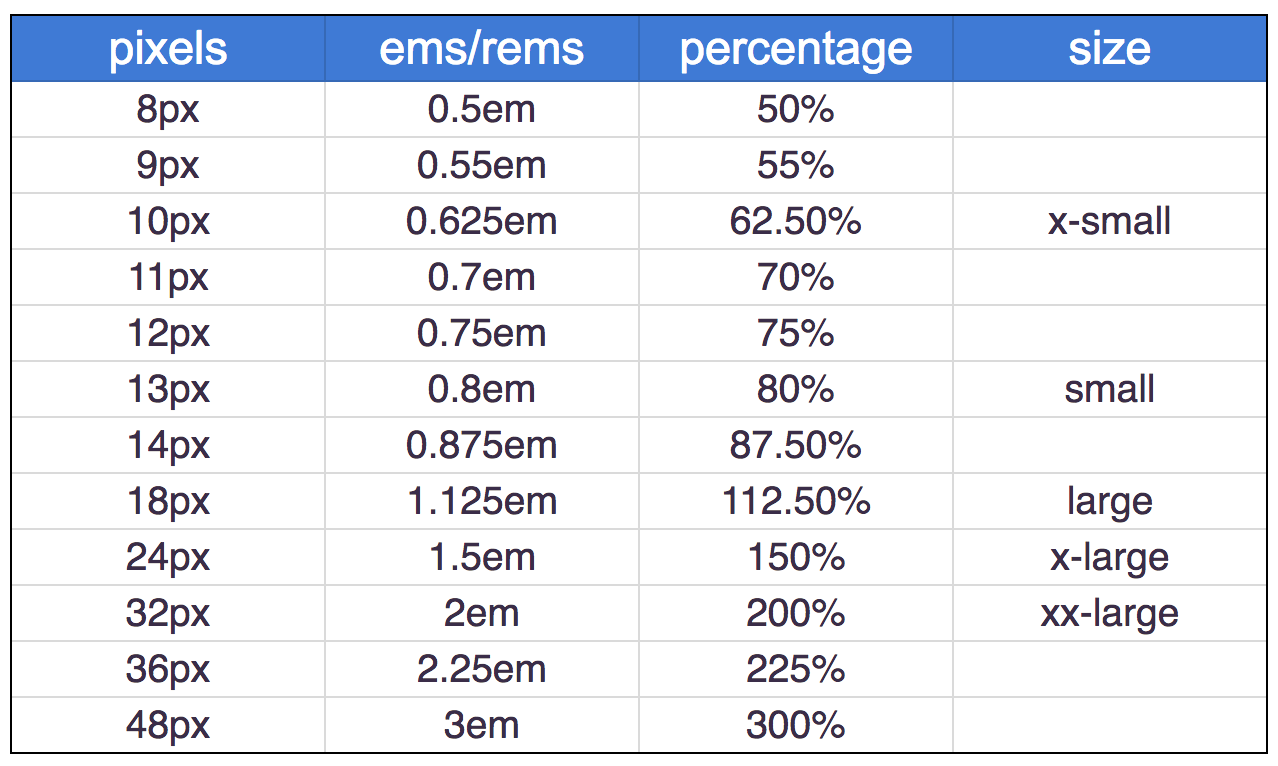
Type Scales
You may have noticed that programs such as Word, Photoshop and InDesign offer the same sizes of text.
It is considered that this scale for type is pleasing to the eye and it has therefore changed little in the last 400 years.
For this reason, when you are designing pages, using sizes from this scale will help them look more attractive.
Units of Type Size
TEXT Summary:
- There are properties to control the choice of font, size, weight, style, and spacing.
- There is a limited choice of fonts that you can assume most people will have installed.
- If you want to use a wider range of typefaces there are several options, but you need to have the right license to use them.
- You can control the space between lines of text, individual letters, and words. Text can also be aligned to the left, right, center, or justified. It can also be indented.
- You can use pseudo-classes to change the style of an element when a user hovers over or clicks on text, or when they have visited a link.